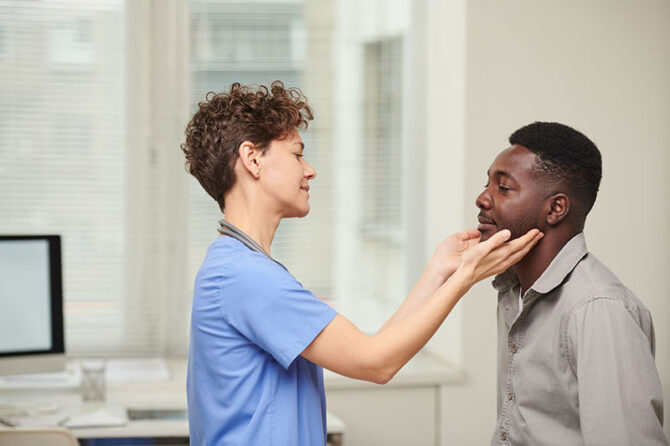

Parotid gland tumours, once a domain exclusive to traditional surgical methods, have witnessed ground-breaking advances in recent times. While the primary objective has always been the effective resection of the tumour, the aesthetic and post-operative implications for the patient have taken centre stage in the recent wave of surgical innovations. The desire to minimize visible scars, reduce postoperative complications, and ensure swift recovery has propelled the exploration of new techniques in parotid surgery. One such pioneering technique is the endoscope-assisted resection via concealed post-auricular sulcus incision. In this article, Yuke Dong, MD et al., illuminate the recent advancements in this innovative procedure, leveraging their extensive research published in Laryngoscope.
Standard treatment for salivary gland tumours, especially those within the parotid gland, historically utilized the “S”-shaped Blair incision, ensuring effectiveness but with a trade-off – a conspicuous scar. Contrarily, the endoscope-assisted technique, a brainchild of Lin et al. from 2000, taps into the concealed post-auricular sulcus incision, melding efficacy with aesthetic appeal.
A comprehensive study was executed at the esteemed Department of Otolaryngology, Zhengzhou Central Hospital between October 2019 and March 2021. It encompassed benign parotid gland tumour patients fitting a rigorous criterion. These patients were then grouped either for the endoscope-assisted procedure or the traditional technique, ensuring identical post-operative care for both.
Endoscope-Assisted Approach, incorporating an incision behind the ear, utilized an endoscope for precise operations, ensuring minimal interference with the facial nerve. The post-surgical area was sealed using a muscle flap from the sternocleidomastoid.
Of the 45 patients, 24 underwent the endoscope technique while 21 experienced the conventional approach. The former demonstrated superior results in terms of shorter incision lengths, diminished intraoperative blood loss, and expedited recovery, with no significant hike in post-operative complications. Furthermore, patients from the endoscope cohort expressed higher satisfaction with their post-surgical appearance.
Evolution of Surgical Methods, from the rudimentary tumour enucleation, marred with high recurrence, transitioned to advanced methods like superficial parotid lobectomy and total parotidectomy, decreasing recurrence but intensifying complications. Partial superficial lobectomy has emerged as the frontrunner, balancing outcomes and safety.
Aesthetic implications of surgical interventions have garnered importance, as they can significantly influence a patient’s self-perception and psychological health. Concealed incisions, especially with the advent of endoscopic technology, have revolutionized head and neck surgeries. Leveraging magnification, illumination, and thermal equipment associated with endoscopes, surgeries achieve precision with minimized bleeding.
Despite its advantages, endoscopic surgery presents hurdles, including limited operational space and complexities with larger tumors. The procedure requires significant expertise, state-of-the-art equipment, and seamless teamwork.
The rigorous research design and extensive comparative data are the study’s cornerstone. While the study is not without its limitations, such as a single-center sample size, it underscores the profound implications of concealed incision surgery, particularly emphasizing rapid recovery and heightened patient satisfaction.
The evolution of parotid surgery reflects the medical community’s commitment not just to treat, but to enhance the overall patient experience. The endoscope-assisted resection of benign parotid tumours via a concealed post-auricular sulcus incision epitomizes this commitment. Yuke Dong, MD and colleagues have provided invaluable insights into this surgical approach, emphasizing its efficacy, safety, and cosmetic advantages. As outlined in their work in Laryngoscope, this procedure promises a paradigm shift in the treatment of parotid tumours, setting the stage for a future where surgical excellence converges with an enhanced patient aesthetic and psychological well-being.
References /. Please access complete paper at the following link:
Dong, Y., Zhang, J., Li, Y., Huang, W., Dang, Y., Gong, W., Shen, X., & Xu, L. (2022). Endoscope‐Assisted Resection of Benign Parotid Tumors via Concealed Post‐Auricular Sulcus Incision. The Laryngoscope, 133. DOI: 10.1002/lary.30140
Leave a reply















Prahlada Sir 💐. To summarise the innovative technique of : “ Endoscopic resection of benign parotid tumours “ ……
* Minimally invasive technique
* Enhanced visualisation of the surgical area
* Facial nerve not likely to get damaged
* Faster recovery seen
* Scarring minimal
&
finally …….utmost patient satisfaction….this is what needed & expected 👍🤩💐
Reply